探秘“药食同源” | 药食同源中药材的起源与发展
“药食同源”源于中国传统医学的智慧,指的是一些食物与药物之间存在着相似的成分和功效,食物即药物,有些药物也是食物。药食同源中药材严格来讲是指传统作为食品,且列入《中华人民共和国药典》的药材。药食同源中药材兼具药食两性,可通过“补气”、“扶正”、“固本”实现治“未病”的效果。
《中华人民共和国食品安全法》规定:“生产经营的食品中不得添加药品,但是可以添加按照传统既是食品又是中药材的物质”。中华人民共和国卫生部2002年首次印发《既是食品又是药品的物品名单》,公布了87种药食同源中药材;2014年新増人参、山银花等15种药食同源中药材;2019年新增当归、山奈、西红花、草果、姜黄、荜茇等6种,同时将党参、肉苁蓉、铁皮石斛、西洋参、黄芪、灵芝、天麻、山茱萸、杜仲叶等9种中药材列为试点管理。
国家卫健委现已公布的药食同源中药材名单如下:
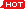
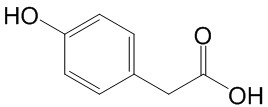
丁香、八角茴香、刀豆、小茴香、小蓟、山药、山楂、马齿苋、乌梢蛇、乌梅、木瓜、火麻仁、代代花、玉竹、甘草、白芷、白果、白扁豆、白扁豆花、龙眼肉(桂圆)、决明子、百合、肉豆蔻、肉桂、余甘子、佛手、杏仁(甜、苦)、沙棘、牡蛎、芡实、花椒、赤小豆、阿胶、鸡内金、麦芽、昆布、枣(大枣、酸枣、黑枣)、罗汉果、郁李仁、金银花、青果、鱼腥草、姜(生姜、干姜)、枳椇子、枸杞子、栀子、砂仁、胖大海、茯苓、香橼、香薷、桃仁、桑叶、桑椹、桔红、桔梗、益智仁、荷叶、莱菔子、莲子、高良姜、淡竹叶、淡豆豉、菊花、菊苣、黄芥子、黄精、紫苏、紫苏籽、葛根、黑芝麻、黑胡椒、槐米、槐花、蒲公英、蜂蜜、榧子、酸枣仁、鲜白茅根、鲜芦根、蝮蛇、橘皮、薄荷、薏苡仁、薤白、覆盆子、藿香、人参、山银花、芫荽、粉葛、布渣叶、夏枯草、当归、山奈、西红花、草果、姜黄、荜茇……
The list of medicinal and edible homologous Chinese medicines published by the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China is as follows:
Clove, Star anise, Sword bean, Fennel, Silybum marianum, Chinese yam, Hawthorn, Purslane, Black-striped snake, Chinese plum, Papaya, Hemp seed, Chinese alangium, Solomon's seal, Licorice, Chinese angelica, Ginkgo nut, Kidney bean, Longan fruit flesh, Cassia seed, Lily, Cinnamon, Chinese matrimony vine fruit, Finger citron, Apricot kernel, Sea buckthorn, Oyster shell, Euryale seed, Sichuan peppercorn, Adzuki bean, Donkey-hide gelatin, Gizzard lining, Barley sprout, Kelp, Jujube (red dates, sour jujube, black jujube), Monk fruit, Prunus seed, Honeysuckle, Houttuynia cordata, Ginger (fresh ginger, dried ginger), Zhi ju zi, Chinese wolfberry, Amomum fruit, Sterculia seed, Poria, Citron fruit, Mosla herb, Peach kernel, Mulberry leaf, Mulberry fruit, Tangerine peel, Platycodon root, Alpinia fruit, Lotus leaf, Radish seed, Lotus seed, Galangal, Lophatherum leaf, Fermented soybean, Chrysanthemum flower, Chicory herb, Yellow mustard seed, Polygonatum root, Perilla leaf, Perilla seed, Kudzu root, black sesame seed, Black pepper, Sophora fruit, Sophora flower, Dandelion, Honey, Chinese torreya seed, Sour jujube seed, Fresh imperata root, Fresh Phragmites root, Chinese pit viper, Tangerine peel, Peppermint, Coix seed, Chinese leek bulb, Raspberry fruit, Pogostemon herb, Ginseng, Honeysuckle flower, Coriander, Pueraria root, Sparganium leaf, Prunella herb, Chinese angelica root, Herba ecliptae, Safflower, Amomum fruit, Turmeric, Piper longum…
药食同源药材在安全性与药用价值方面具有得天独厚的优势,是中医治“未病”的主要手段之一,也是中药现代化的一个重要研发方向。在中医药理论的指导下,辅以现代科学技术与方法,充分挖掘药食同源资源宝库,进一步强化药食同源中药材的开发利用,有助于中药现代化的推进,有助于提升人民的健康福祉。